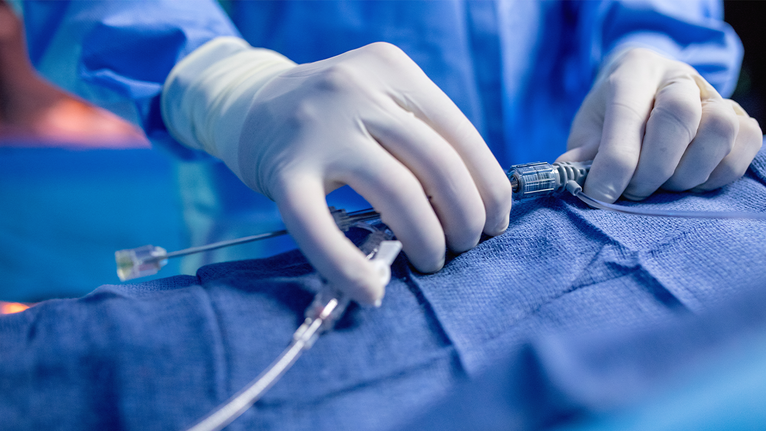
No one looks forward to surgery. Even today, surgery is a major medical treatment needing days in the hospital, followed by weeks of recovery at home. Surgery requires incisions (cuts) that can sometimes leave large wounds that may be painful and take a long time to heal. A lot has changed in the medical field in the last 30 years. Advances in medical technologies have made it possible for procedures that need much smaller incisions than the corresponding open surgery procedure. Procedures that do not involve large cuts into the body are known as minimally invasive procedures.
Interventional radiologists were the pioneers of minimally invasive procedures. They introduced angioplasty and the catheter-delivered stent. Today, many conditions that once required surgery can be treated non-surgically.
In traditional open surgery, your surgeon makes one large cut to see the part of your body they are operating on and does the appropriate procedure. In minimally invasive procedures, doctors use small tools, cameras, and lights that fit through several tiny cuts in your skin. Special medical equipment such as fibre optic cables, miniature video cameras and special instruments handled via tubes are inserted into the body through small openings on the surface. The images of the interior of the body are transmitted to an external video monitor.

It is now possible to treat a range of common conditions using minimally invasive procedures. A minimally invasive procedure may be a good option for treating existing health conditions such as varicose veins, fibroids, prostrate, and thyroid.
Advantages of minimally invasive operating techniques
Less pain
Faster recovery
Quicker return to work
Little scarring

This is not true. Over the years, as scientists have better understood cancer, there have been vast improvements in treatments, and recovery rates continue to improve. Many forms of cancer, depending on when they’re caught, are treatable and curable. Some forms of cancer are even curable at advanced stages.
No – You cannot catch cancer from another person. Not through contact or secretions or anything in the air. Cancer is not contagious. Some infections, such as sexually transmitted diseases, can cause cancers in the cervix and the liver, but the cancer itself is not contagious.
Advances in equipment used during surgery and more detailed imaging tests have helped make this risk very low.
There are many types of cancer which you are more likely to develop if someone in your family has had them. However, cancers can be caused by changes to your DNA that happen over the course of your lifetime in response to changes in your environment or the ageing process.
Most lumps detected during screenings and medical examinations are benign or a different condition, such as a cyst. A doctor will conduct tests to determine whether a growth is benign, precancerous, or cancerous.
While traditional medicine may help manage the side effects of conventional treatments and improve overall well-being, surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation have a clear and established role in acute cancer management.
