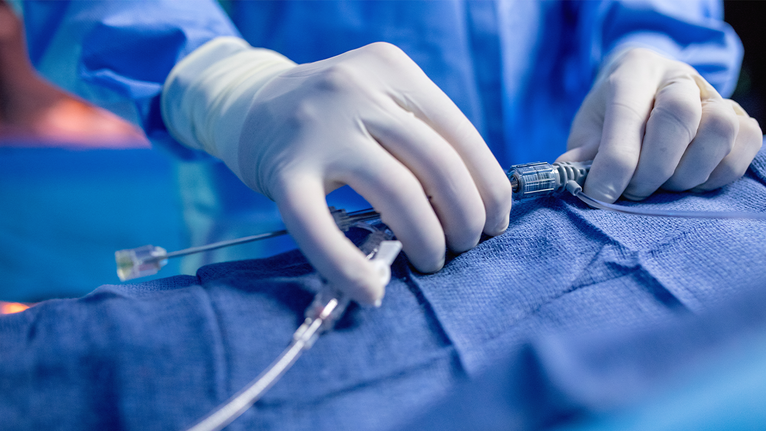
No one looks forward to surgery. Even today, surgery is a major medical treatment needing days in the hospital, followed by weeks of recovery at home. Surgery requires incisions (cuts) that can sometimes leave large wounds that may be painful and take a long time to heal. A lot has changed in the medical field in the last 30 years. Advances in medical technologies have made it possible for procedures that need much smaller incisions than the corresponding open surgery procedure. Procedures that do not involve large cuts into the body are known as minimally invasive procedures.
Interventional radiologists were the pioneers of minimally invasive procedures. They introduced angioplasty and the catheter-delivered stent. Today, many conditions that once required surgery can be treated non-surgically.
In traditional open surgery, your surgeon makes one large cut to see the part of your body they are operating on and does the appropriate procedure. In minimally invasive procedures, doctors use small tools, cameras, and lights that fit through several tiny cuts in your skin. Special medical equipment such as fibre optic cables, miniature video cameras and special instruments handled via tubes are inserted into the body through small openings on the surface. The images of the interior of the body are transmitted to an external video monitor.

It is now possible to treat a range of common conditions using minimally invasive procedures. A minimally invasive procedure may be a good option for treating existing health conditions such as varicose veins, fibroids, prostrate, and thyroid.
Advantages of minimally invasive operating techniques
Less pain
Faster recovery
Quicker return to work
Little scarring